What is range in Python?
ipython
If you can use shell interface, please try with ipython package. This gives you interactive Python. Python does have REPL (Read eval print loop). The ipython package is kind of fancy stuff. It provides you syntax highlighting and nice indentation for writing a function. It’s clearly better than using default REPL. Once you type in Python, it will directly show you what you typed. It gives you better idea what you are trying to do.
ipython
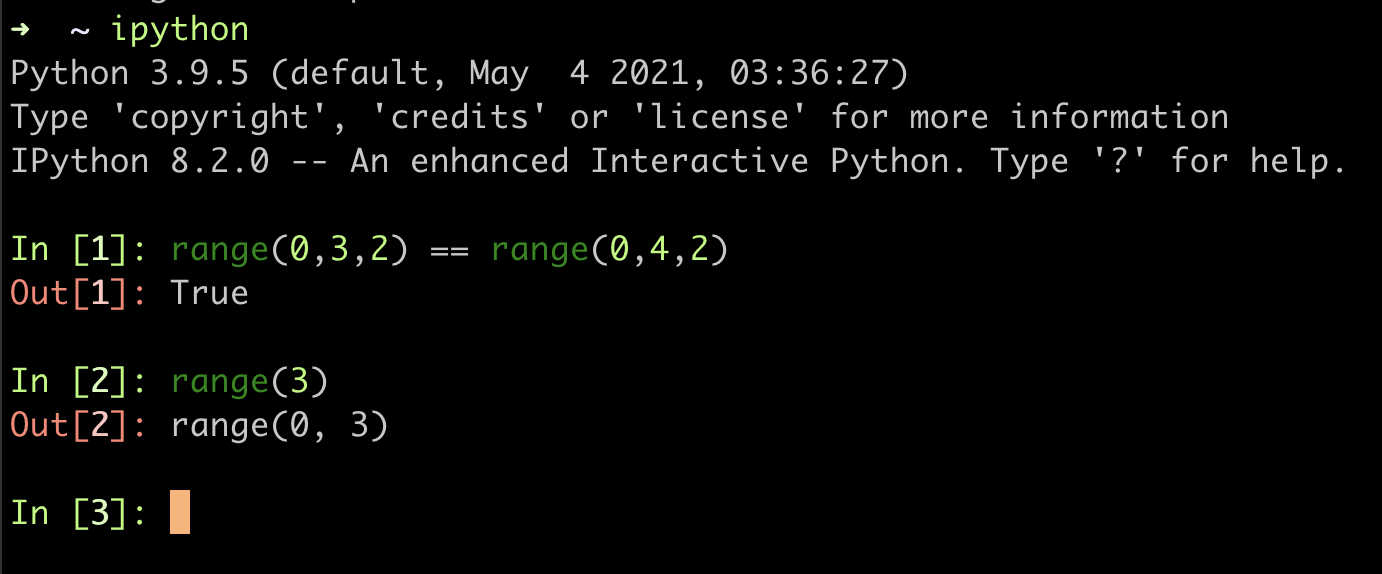
How does look like Range in Python?
I usually use range when I need to iterate list value.
a = [0, 1, 2]
for i in range(len(a)):
print(a[i])
# 0
# 1
# 2
Is this a generator?
No, it’s an “immutable” sequence of numbers. Under the hood, range objects implement collections.abc.Sequence.
What is Immutable?
For myself, the immutability in programming is like a constant variable. When you created a variable with initialized value, you wouldn’t modify the value of the variable.
According to Wiki, Immutable object
In object-oriented and functional programming, an immutable object (unchangeable object) is an object whose “state” cannot be modified after it is created.
State?
This is a great article which explains “state” with daily analogy. “State” in programming means “data”.
“state” cannot be modified after it is created. This means “data” cannot be modified after the object gets created.
Does this mean stateless?
No, “stateless” in programming means there is no data to keep track. In oppositie, it’s called “stateful”.
Grey area; immutable list?
Python doesn’t offer immutable list. In order to use immutable list, you might need to look up tuple. tuple in Python is immutable. In this context, you cannot update its value, append new value, and delete values.
collections.abc.Sequence?
This is the next topic.
Defining range object
range(start, stop[, step])
You can pass integers either built-in int or any object that implements the __index__() special method.
class Custom:
def __index__(self):
return 3
range(Custom()) == range(3) # True
We can only pass stop value like range(3). The start value in default is 0. The default step value is 1.
If we pass 0 to step parameter, it raises ValueError.
range(0, 3, 0) # ValueError: range() arg 3 must not be zero
There are value constraints depending on step parameter.
stepis positive, i-th value of range must meeti >= 0andstart + step * i < stopstepis negative, i-th value of range must meeti >= 0andstart + step * i > stop
range(3)
# (0 >= 0 and 0 + 1 * 0 < 3) == True
# (1 >= 0 and 0 + 1 * 1 < 3) == True
# (2 >= 0 and 0 + 1 * 2 < 3) == True
# (3 >= 0 and 0 + 1 * 3 < 3) == False
range(3, 0, -1)
# (0 >= 0 and 3 + -1 * 0 > 0) == True
# (1 >= 0 and 3 + -1 * 1 > 0) == True
# (2 >= 0 and 3 + -1 * 2 > 0) == True
# (3 >= 0 and 3 + -1 * 3 > 0) == False
When the first element doesn’t meet the value constraints, the range object will be empty.
len(range(3, 0, 1)) == 0 # True
Range raises OverflowError if we pass larger than sys.maxsize.
import sys
max_range = range(sys.maxsize + 1)
len(max_range) # OverflowError
Operation with range
Let’s say s is a range object. x, i, j, k are integers. We can use;
x in sx not in ss[i]s[i:j]s[i:j:k]len(s)min(s)max(s)s.index(x[,i[,j]])s.count(x)
Advantage
The range will always take the same (small) over a regular list or tuple since it only stores start, stop, and step values.



Leave a comment