Django rest framework
Django rest framework
In this post, we want to look through the django rest framework. When we face building an API service in Django, we might check out the Django rest framework. If you want to see quickly, please take a look at this commit.
Install
# install the django rest framework
$ pip install djangorestframework
# verify the installation
$ pip list | grep djangorestframework
# djangorestframework 3.11.0
# mysite/settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'polls.apps.PollsConfig',
'rest_framework', # added
]
Please install the Django rest framework by using pip command. We can verify the installation by using the second command. If we install it, we need to integrate the framework into our project.
Serializer
from .models import Question, Choice
from rest_framework import serializers
class ChoiceSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Choice
fields = ('question', 'choice_text', 'votes')
class QuestionSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
choice_set = ChoiceSerializer(many=True, read_only=True)
class Meta:
model = Question
fields = ('question_text', 'pub_date', 'choice_set')
Please understand that we are starting from the polls tutorial from the Django official document. Alternatively, we can find the polls tutorial repository from this commit. If you need it, please feel free to use.
“Serializers allow complex data such as querysets and model instances to be converted to native Python datatypes that can then be easily rendered into JSON, XML or other content types.” This quote from the django rest framework document about serializer.
“Serialization is a mechanism of converting the state of an object into a byte stream.” This quote is from here.
API view
from .models import Question, Choice
from rest_framework import viewsets
from .serializers import QuestionSerializer, ChoiceSerializer
class QuestionViewSet(viewsets.ModelViewSet):
queryset = Question.objects.all().order_by('-pub_date')
serializer_class = QuestionSerializer
class ChoiceViewSet(viewsets.ModelViewSet):
queryset = Choice.objects.all()
serializer_class = ChoiceSerializer
We can find the APIView class is in the framework. In a nutshell, this view inherits Django’s generic.View class, but this view doesn’t have the post, get, and other HTTP request method. In detail, please find this document.
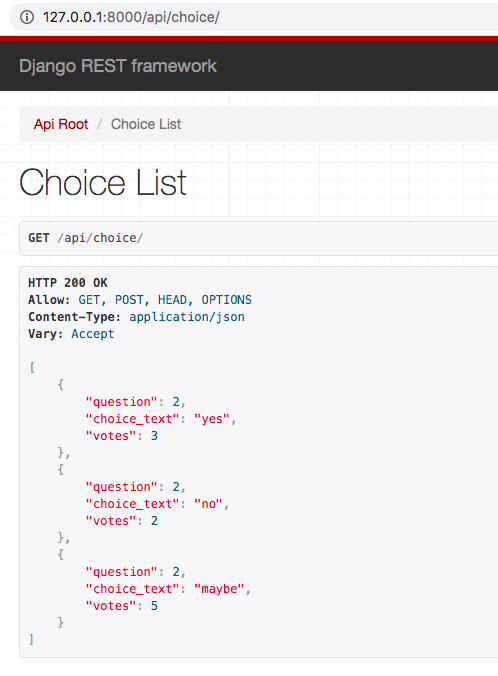
This implementation will show the above image to us and it will be a handy guideline about how to use this API.
URL config
# mysite/urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
from django.contrib.auth import views
from rest_framework import routers
from polls import api_views
router = routers.DefaultRouter()
router.register(r'question', api_views.QuestionViewSet)
router.register(r'choice', api_views.ChoiceViewSet)
urlpatterns = [
path('polls/', include('polls.urls')),
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('api/', include(router.urls)),
path('api/', include('rest_framework.urls',
namespace='rest_framework'))
]
The final step is wiring all the required things in the url configuration file.



Leave a comment